
Postdoc work (Nanjing, China)
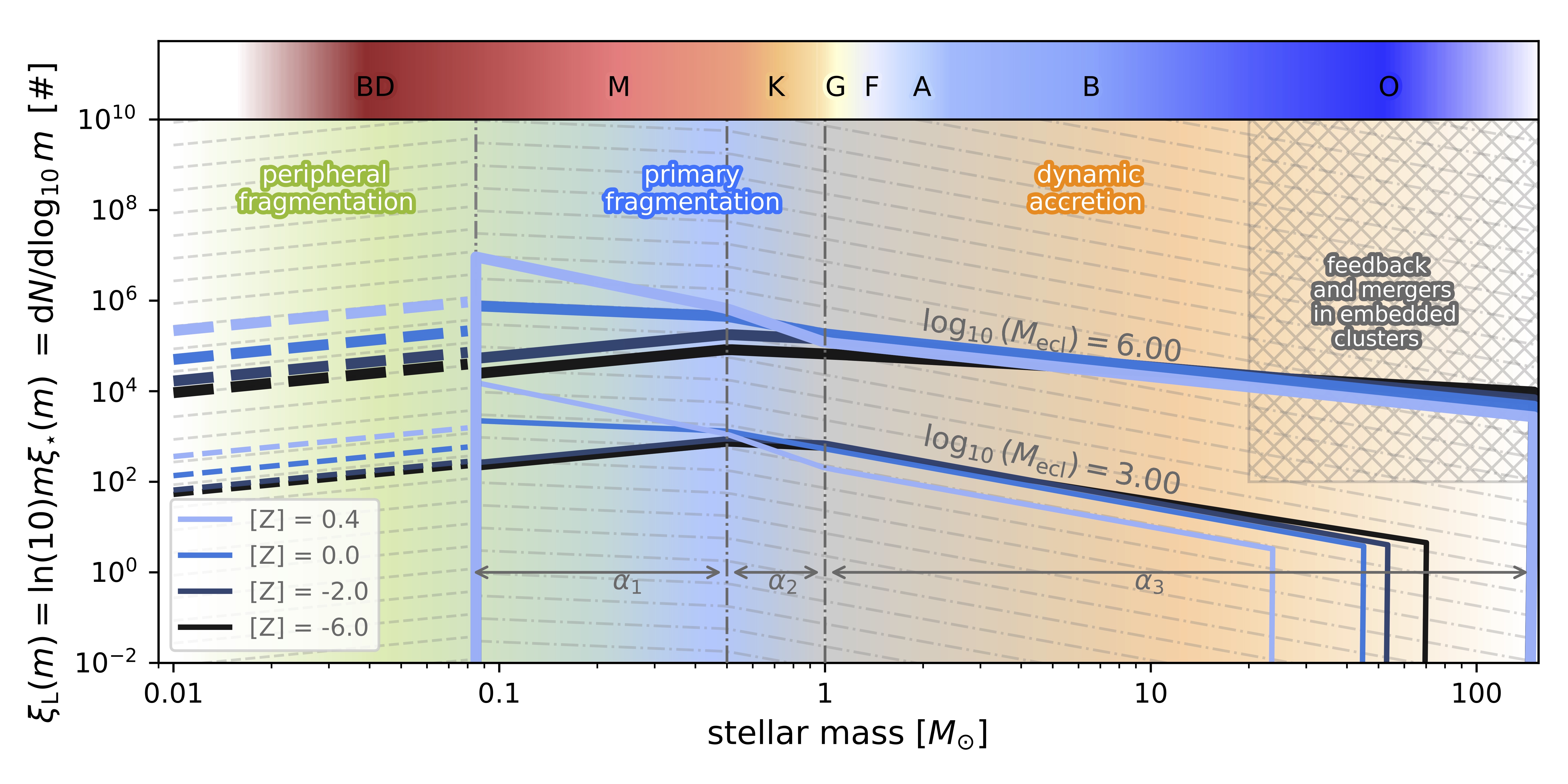
IMF
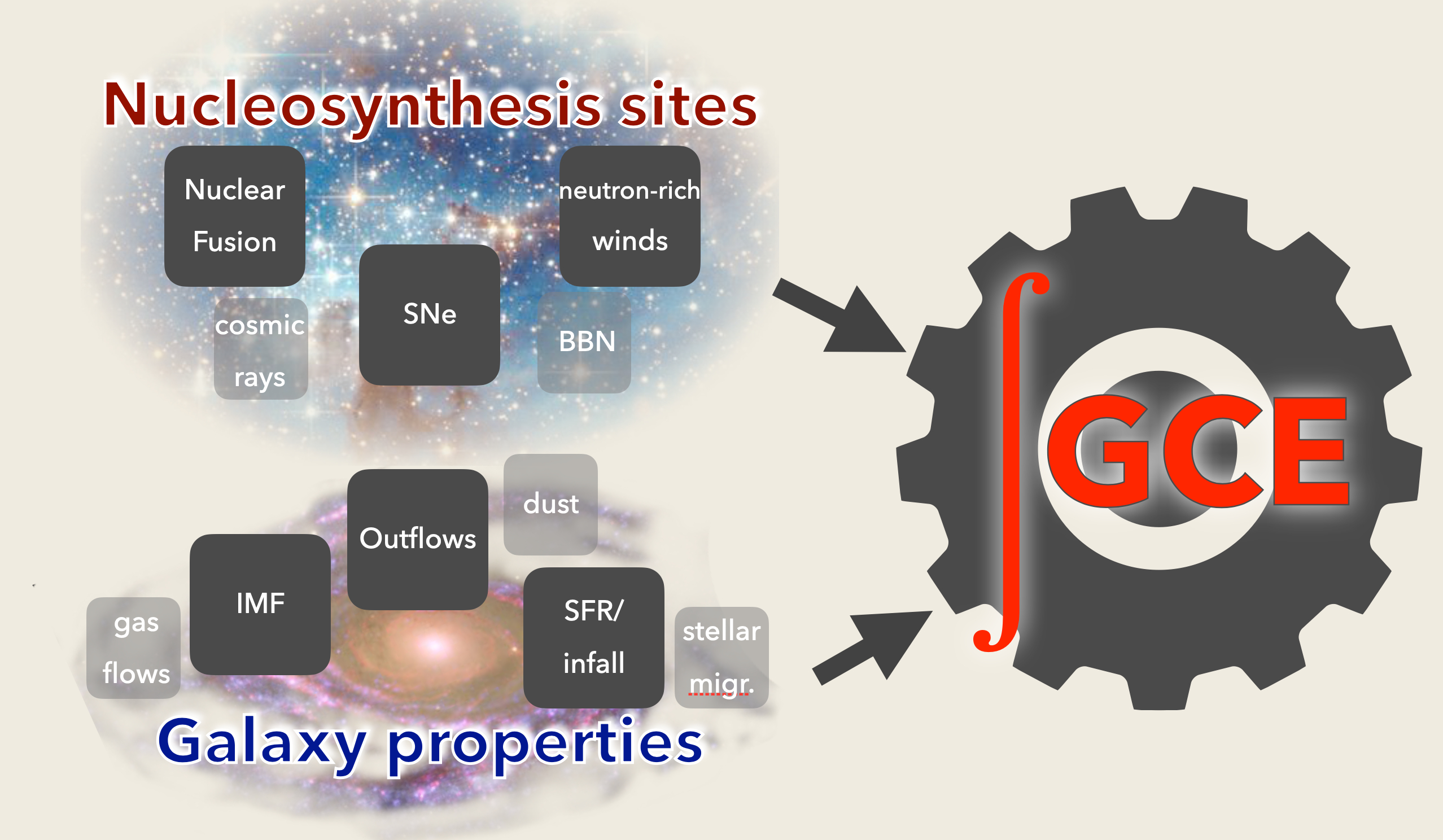
The Initial Mass Function (IMF) is one of the most important relations in astrophysics. Almost every inferred property of a stellar population is an integral over the IMF.
Stars form from the collapse of dense, cold clumps in molecular clouds. These conditions do not occur in isolation, rather they arise in clustered environments. Consequently, also stars do not form in isolation but during star-forming episodes where a single stellar population (SSP) is born. The number distribution of newly born stars as a function of mass is the stellar IMF.
Stars are not born simultaneously. Any given SSP will produce its stars within about one million years. Therefore, the stellar IMF is not an observable quantity. It is instead a theoretical curve that represents the full stellar birth history of a SSP.
Multiple SSPs may form within similar timframes in a molecular cloud, and a galaxy may host several such clouds at once. For distant galaxies where individual stars are unresolved, it is important to distinguish between the stellar IMF of an SSP and the cumulative sum of many SSPs formed within a similar timeframe. This cumulative distribution is the galaxy-wide IMF.
IGIMF
The Integrated Galaxy-wide Initial Mass Function (IGIMF) theory is being developed since 2002.
It assumes that all stars form in SSPs. A galaxy’s average properties determine the mix of SSPs that form within a short 10 Myr interval. The IGIMF framework then determines the galaxy-wide IMF from these properties.
The IGIMF theory is also among the first to recognize and quantify the variability of the IMF.
Moreover, the IGIMF theory is providing theoretical insights on the yet-unknown physical mechanisms that trigger star formation in dense gas clumps.
See the monograph chapter to appear in Elsevier’s Encyclopedia of Astrophysics for an overview of the field.
You can compute the IGIMF as a function of average star formation rate and metallicity using the code presented in this RAA paper, which also outlines milestones of the IGIMF theory.